Application Notes

High Voltage Power Supplies

There is no universally accepted definition of how high a voltage must be in order to be considered a high voltage, though a power supply with an output of 1,000 volts or more is virtually always considered to be High Voltage Power. Likewise, one with an output between 0 and 100 volts is virtually always considered to be a low voltage power supply. Identifying a power supply with a voltage between 100 volts and 1,000 volts as a low or high voltage power supply is often influenced by the application.
High voltage power supplies are typically capable of voltage and current regulation and are adjustable from 0VDC to rated output voltage and from 0ma to rated output current. For safety reasons, the return of the high voltage DC output is generally connected to chassis ground.
Acopian High Voltage power supplies may be used as constant voltage or constant current sources. They may be remotely programmed by means of either voltage or resistance, and have provisions for remote monitoring and output inhibiting. All control and monitoring connections on our modular high voltage power supplies are on a pluggable terminal block that functions as a connector, providing wiring convenience and permitting easy and rapid connect/disconnect. Outputs are arc/short circuit protected.
What is a current regulated high voltage power supply?
Typical high voltage power supplies are voltage regulated, which means that the output voltage will remain constant throughout the output current range. Acopian’s high voltage power supplies can be voltage regulated or current regulated, depending on the load and power supply settings. For example, imagine a 10000VDC, 0.03A high voltage power supply with a connected load that draws 0.02A at 10000V. If the Vadj and Iadj pots are fully clockwise, the power supply will regulate the voltage at 10000VDC and the output current will be 0.02A. If the Vadj pot is slowly turned counterclockwise, the output voltage will track the pot setting. If it is left at 5000VDC, the output will remain at 5000VDC and the current will be reduced to 0.01A. Current regulation mode is different. Leave the Vadj pot fully clockwise and turn the Iadj pot counterclockwise. When the Iadj reaches 0.02A, the power supply will start to current regulate. As the Iadj pot is turned lower, the output voltage will start to decrease to maintain the current that the Iadj pot is set at. If it is left at 0.01A, the output current will remain at 0.01A, the output voltage adjusting to the voltage required to keep it at 0.01A (5000V in this case).
Can two Acopian high voltage power supplies be connected in series for increased voltage?
Acopian’s high voltage power supplies do not have an isolated output - for safety reasons, the return is connected to chassis ground. High voltage power supplies cannot be connected in series or parallel.
Can Acopian high voltage power supplies be connected in either polarity?
Generally, no. Acopian high voltage power supplies do not have an isolated output - for safety reasons, the return is connected to chassis ground. If your load is grounded, then you cannot reverse the polarity. Acopian high voltage power supplies can be ordered with either a negative or positive output polarity, the prefix on the model number being either an N or a P as required.
How do I measure the output voltage and current produced by my high voltage power supply?
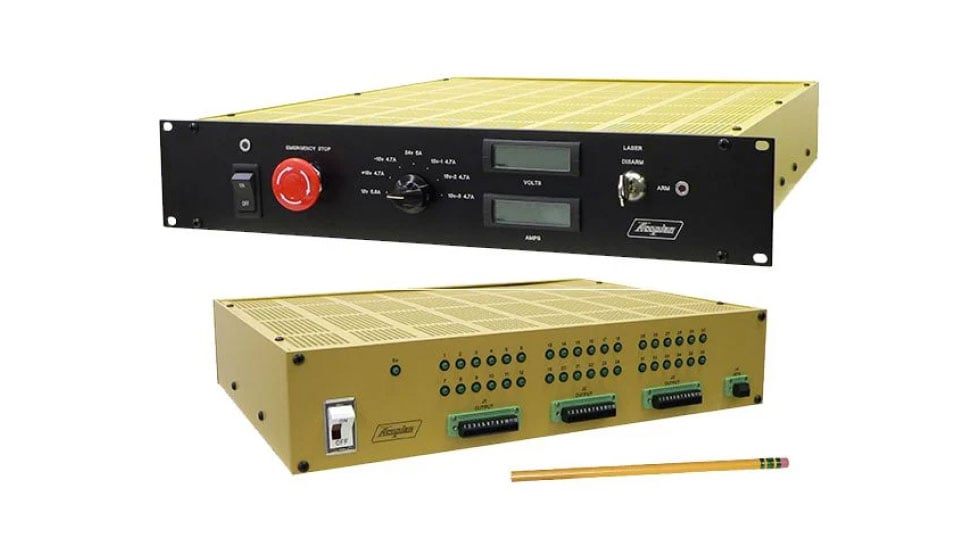
Acopian’s rack mounted high voltage power supplies have a built-in analog voltmeter and ammeter to measure output volts and amps. All Acopian high voltage power supplies have current and voltage monitoring output signals. A standard digital multimeter capable of directly reading volts and millivolts is all that is needed.
Acopian high voltage power supply models:
- AC-DC High Voltage Power Supply - Modular
- 30 - 60 Watts
- 1000 - 30000 volts output models
- Constant voltage or current
- Remote programming, monitoring, and inhibit
- Pluggable terminal block
- Arc/short circuit protected
- DC-DC High Voltage Power Supply - Modular
- 30 - 60 Watts
- DC input from 21.6V to 32V
- 1000 - 30000 volts output models
- Constant voltage or current
- Remote programming, monitoring, and inhibit
- Pluggable terminal block
- Arc/short circuit protected
- AC-DC High Voltage Rack Mount Power Supply
- 30 - 60 Watts
- 1000 - 30000 volts output models
- Calibrated 10-turn voltage and current controls
- Voltmeter, ammeter, and handles are standard
- 8’ long shielded output cable
- Constant voltage or current
- Remote programming, monitoring, and inhibit
- Arc/short circuit protected
- Gas discharge tube biasing
- Radiation detection
- Charging particles
- Electrostatic precipitation
- Ozone generation
- Air ionizers

 Made In The USA
Made In The USA

